
Q. I’m planning to swap a Gen. III 5.7L Hemi with an Edelbrock supercharger into a third-gen Dodge D-Series pickup truck. My Question is about the fuel system: How do I determine what size fuel pump I need?
A. To make the proper fuel pump selection, you first need to determine your vehicle’s maximum horsepower. You can make a reasonable horsepower estimate based on the supercharger kit’s advertised power rating or an engine dyno simulation program—erring on the high side to be safe.
Calculating An Engine’s Minimum Required Fuel Flow
A fuel pump’s flow rate is determined by the amount of fuel it can supply over a given time at a specified pressure. Pumps are generally rated in gallons per hour (gph) or liters per hour (lph). The formula for calculating the minimum required flow for your application is accomplished by multiplying peak horsepower by the brake specific fuel consumption (BSFC)—a measurement that estimates fuel consumption in pounds per hour for each horsepower.
Example: A 600 hp forced induction engine with a BSFC of 0.75 would use 450 pounds of fuel per hour (600 x 0.75 = 450 lbs./hr.).
A gallon of fuel weighs approximately six pounds. To figure the gph needed, divide lbs./hr. by six (450/6 = 75 gph).
A liter of fuel weighs about 1.6 pounds. To get lph, divide lbs./hr. by 1.6 (450/1.6 = 281.25 lph).
Average BSFC Ranges
| Naturally Aspirated | Forced Induction | |
|---|---|---|
| Pump Gasoline | 0.45 - 0.50 | 0.60 - 0.75 |
| E85 | 0.63 - 0.70 | 0.84 - 1.05 |
| Methanol | 0.90 - 1.00 | 1.20 - 1.50 |
***
Understanding Fuel Pressure & Flow Rate
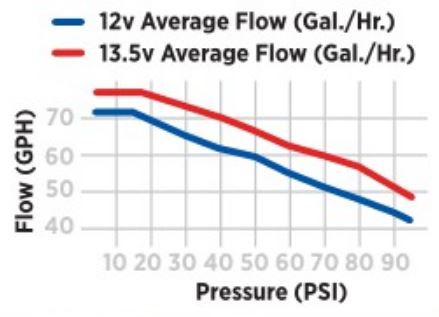
As pressure increases, flow rate decreases. Some pumps are rated at free flow, some at a specific psi, and others are rated in a range for carbureted or fuel injected systems.
When selecting a pump, make sure it can support the volume needed at your system’s required pressure.
General Guidelines for Fuel Pump Selection
| Fuel Pump Free Flow | Carbureted Engine | Carbureted Engine with Power Adder | Fuel Injected Engine | Fuel Injected Engine with Power Adder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 gph/114 lph | 350 hp | 300 hp | 300 hp | 250 hp |
| 40 gph/155 lph | 450 hp | 400 hp | 400 hp | 300 hp |
| 50 gph/190 lph | 600 hp | 500 hp | 500 hp | 400 hp |
| 67 gph/255 lph | 750 hp | 650 hp | 650 hp | 500 hp |
| 90 gph/340 lph | 1,000 hp | 850 hp | 850 hp | 600 hp |
| 125 gph/470 lph | 1,300 hp | 1,000 hp | 1,000 hp | 800 hp |

Comments